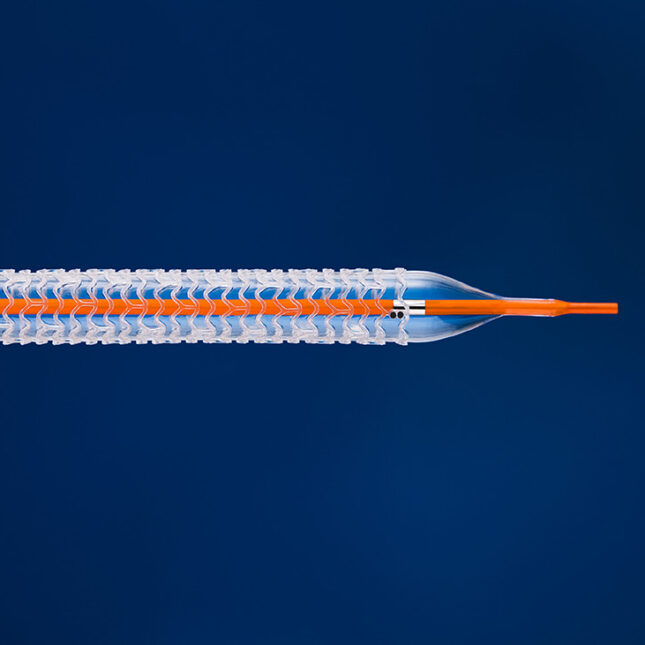
An Abbott device that failed heart disease patients is getting a new life in patients with severe vascular disease.
The device is a below-knee stent that widens clogged blood vessels, and then vanishes into the vessel’s walls over the course of three years. It also delivers a drug that prevents scar tissue from forming — a common risk factor with traditional metal stents that further narrow the vessel.
Abbott’s first dissolvable stent, for coronary artery disease, received Food and Drug Administration approval in 2016. But the company voluntarily pulled the product from the market just over a year later due to “low commercial uptake.” The device also received mixed results in clinical trials.
This article is exclusive to STAT+ subscribers
Unlock this article — and get additional analysis of the technologies disrupting health care — by subscribing to STAT+.
Already have an account? Log in
Already have an account? Log in
To submit a correction request, please visit our Contact Us page.











STAT encourages you to share your voice. We welcome your commentary, criticism, and expertise on our subscriber-only platform, STAT+ Connect